About PASCAL International Observatory
PASCAL International Observatory is a global alliance of researchers, policy analysts, decision makers and locally engaged practitioners from government, higher education, non-governmental organisations (NGOs) and the private sector. It is organised around university centres in Africa (University of Johannesburg), Asia (University of the Philippines), Australasia (RMIT), Europe (University of Glasgow), and the US (Rutgers University), each responsible for its activities in that geographical region. A number of these centres also have sub-centres in other areas of the continent to which they devolve responsibility for certain foci of the observatory. Collectively PASCAL provides an observatory role through interpreting emerging approaches to city and regional development and helps mobilise this knowledge as a basis for policy action. Each of its centres also leads research and development projects related to its key focal points: place, social capital and learning cities. A selection of the projects led by its hub universities are found in the Projects section, alongside other services that PASCAL provides.
PASCAL has its origins in a major conference organised by the OECD in Melbourne in 2002 on the importance of learning cities and regions for regional development. PASCAL's focus is on the development and renewal of place. It gives special emphasis to the role of social capital and lifelong learning in these processes, considering how sustainable economic, social and cultural development can be achieved to the benefit of the communities concerned.
PIMA, the PASCAL International Member Association, grew out of PASCAL. It is global network of experienced individual adult learning and education professionals, with an active interest especially in the different dimensions and contexts of lifelong, wide and deep learning. It supports and participates in the organisational activities of PASCAL and other bodies, in the interests of greater social, economic and ecological justice locally and globally.
But PASCAL is also focussed on the sharing of ideas and knowledge for practical application by cities and regions, recognising that it is at this level that often the greatest impact of policy action can be achieved and efforts made to secure regional competitive advantage. The overarching PASCAL themes are therefore also being developed in ways which address particular policy fields and processes to achieve sustainable change across economic, social and cultural domains.
PASCAL works in collaboration with city and regional and leaders to design and implement development strategies that balance economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental sustainability and place learning at the centre of urban and regional policy.
What PASCAL Stands For
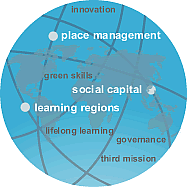
The clue to the focus PASCAL brings to this work is in its name:
PASCAL = Place And Social Capital And Learning
The guiding themes in PASCAL's work relate to:
- The making and management of PLACE. Place management refers to coordinated efforts undertaken by the “shareholders” within a geographic region. By collaboratively linking local assets – built, cultural, financial, human, natural, political, and social – shareholders can improve life in their cities and geographic regions. Cities and multi-jurisdictional regions drive the new economy, so it’s important to think, act, learn, and measure in ways related to the context in which we all want to flourish.
- The promoting of SOCIAL CAPITAL and socially inclusive policies and practices. Regions that are socially inclusive have more inputs – and can generate more complex activities – for creating balanced development. Cities and regions that encourage boundary spanning collaboration are more sustainable and are better at competing in the global economy.
- The development of LEARNING CITIES and REGIONS. Internally collaborative cities and regions facilitate lifelong learning and promote knowledge sharing. PASCAL uses cutting edge research and timely data to better link educational institutions, government, NGOs and the private sectors. We champion both formal and informal learning as essential drivers of innovation.
- The development of the role of Higher Education Institutions(HEIs) in fostering inclusive learning cities and economic and social innovation.
Observatory Activities
PASCAL's key role as an international observatory is based on investigation, analysis and synthesis of global initiatives, mobilising knowledge for action, and policy analysis.
- INVESTIGATION, ANALYSIS and SYNTHESIS - PASCAL gathers, interprets, and shares globally informed analyses of innovative city and regional development. We are organized for networking, knowledge creation, and showcasing initiatives that embrace our guiding themes. PASCAL prepares periodic Papers and Policy Briefs, publishes books, and hosts conferences, seminars, workshops and webinars. Through its Learning Cities Network and Special Interest Groups it provides opportunity for discussion and sharing of emerging practice. Our family of websites, supported through our social media presence, serve as an accessible clearing house and resource base for up-to-date news, information, comment and analysis of city and regional development policies and practice examples from around the world. Subscribers receive a weekly digest of new web content by email.
- MOBLISING KNOWLEDGE FOR ACTION - PASCAL helps city leaders work towards their aspirational goals, and helps cities and regions to realise their potential and take their place in the modern globalised world. The PASCAL network includes expert Associates from around the world, including individuals with senior-level experience in government, higher education, NGOs, and the private sector.
- POLICY - PASCAL’s approach to policy analysis is to work alongside city and regional leaders to help them identify where to concentrate their strategic development efforts through systematic benchmarking and appraisal. The PASCAL network scans the knowledge horizon to track global trends and identify practices that support development objectives, appropriate to context, and which foster both measurement and accountability.
 Printer-friendly version
Printer-friendly version- 3023 reads